Technologies
Importance of Reliability Laboratories
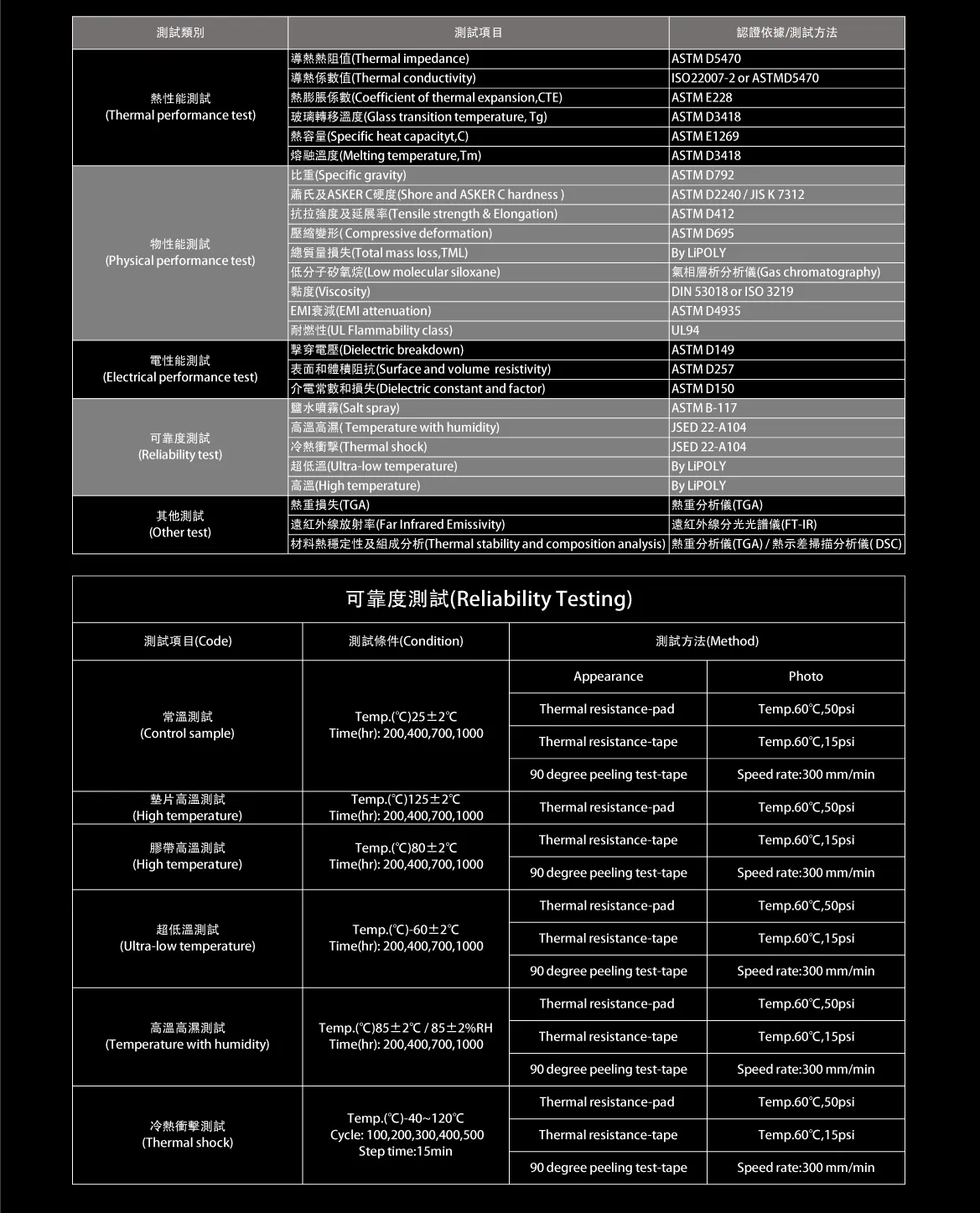
Reliability laboratories comprehensively simulate product performance under extreme conditions through high-temperature aging, low-temperature freezing, and thermal shock tests. These tests not only help manufacturers identify potential issues in advance but also enhance product quality and market competitiveness. Choosing the right instruments and adhering to standard specifications are key to ensuring precise and meaningful test results.

Testing Standards and Applications
High-Temperature Aging Test
High-Temperature Aging Testare primarily used to simulate the performance changes of materials or products under prolonged exposure to high-temperature environments, making them suitable for testing the durability of electronic components, plastics, rubber, and other materials.
Instrument Features:
- Temperature Range:Generally from room temperature to 200°C, with optional higher ranges (such as 300°C).
- Control Precision:Utilizes PID automatic temperature control systems with accuracy up to ±0.3°C.
- Application Ranges:Widely used for lifespan evaluation of electronic products, automotive components, and materials.
Test Objectives:
- Evaluate the aging rate and performance changes of materials.
- Ensure product stability and reliability in high-temperature environments.
Low-Temperature Freezing Test
Low-Temperature Freezing Tests simulate product performance in extremely low-temperature environments, suitable for aerospace, medical equipment, and other applications requiring low-temperature resistance.
Instrument Features:
- Temperature Range:Can reach as low as -70°C to 150°C.
- Cooling Technology:Uses liquid nitrogen or environmentally friendly refrigerants to ensure rapid cooling and stable maintenance of low temperatures.
- Application Ranges:Widely applied to low-temperature performance testing of metals, plastics, electronic components, and other materials.
Test Objectives:
- Test the mechanical properties of materials at extremely low temperatures, such as brittleness and fatigue characteristics.
- Ensure operational stability of products in cold environments.
Thermal Shock Test
Thermal Shock Tests are designed to assess product reliability under rapid temperature switching between extreme high and low temperatures, particularly suitable for detecting physical damage or performance changes caused by thermal expansion and contraction.
Instrument Features:
- Temperature Range:High temperature up to 200°C, low temperature down to -70°C.
- Switching Speed:Complete high-low temperature zone switching within 10 seconds.
- Structural Design:Utilizes three-chamber or two-chamber design for efficient hot-cold switching.
Test Objectives:
- Simulate rapid changes under extreme climate conditions.
- Detect cracks, deformations, or other damage caused by thermal expansion and contraction.
Conclusion
The three tests—high-temperature aging, low-temperature freezing, and thermal shock—constitute indispensable core components of reliability laboratories. Through these precise instruments and methods, companies can comprehensively assess product performance under various extreme environments, thereby enhancing durability and market competitiveness.
| TEST METHOD | PROPERTY | Instrument Types | Application Ranges |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM D5470 | Thermal Conductivity/Resistance | TIM Tester | High Thermal Conductivity TIM Materials |
| ASTM D374 | Thickness | Electronic Thickness Gauge | Thickness Changes After Phase Transition |
| ASTM D792 | Density | Density Meter | Impact of Filler Content on Performance |
| ASTM D2240 | Hardness | Shore Hardness Tester | Pressure-Based Material Selection |
| ASTM D149 | Dielectric Breakdown | Hipot Tester | High Voltage Performance Analysis |