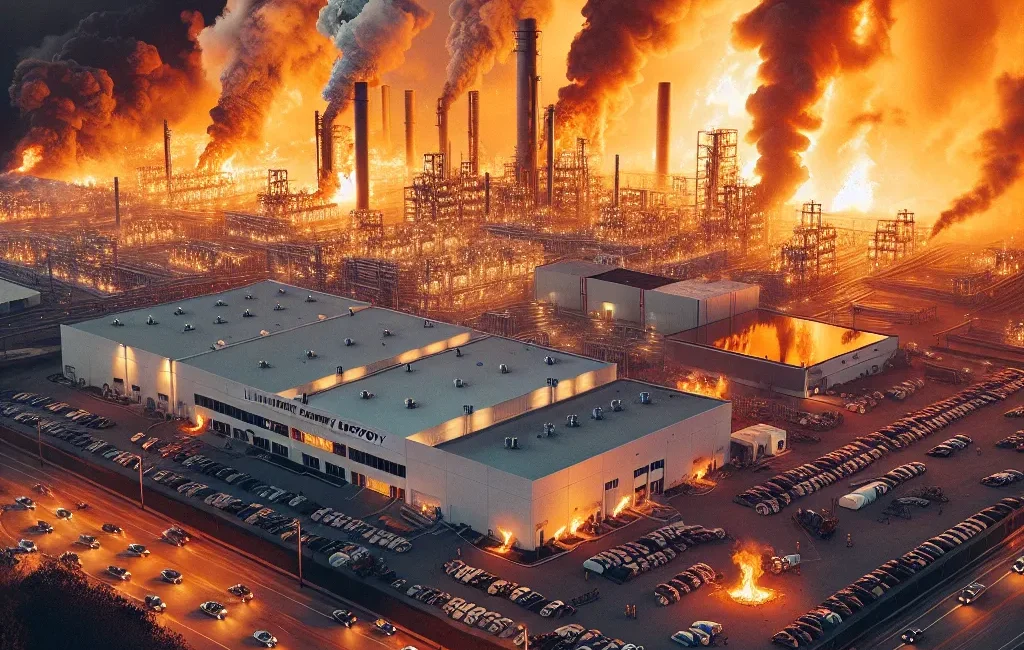
Serious Consequences of Battery Thermal Runaway
Thermal runaway is an autocatalytic process that triggers uncontrollable exothermic reactions when battery temperature rises to a certain level.
This phenomenon can lead to the following serious consequences:
Toxic Gas Release:
During thermal runaway, batteries may release toxic gases such as hydrogen fluoride (HF), posing serious threats to human health.
Fire and Explosion Risk:
Rapid temperature rise may cause battery ignition and even lead to explosions.
Chain Reaction:
In large-scale energy storage facilities or electric vehicle battery packs, thermal runaway of one battery may trigger a chain reaction in adjacent batteries, causing more extensive disasters.
Environmental Pollution:
Toxic smoke from fires may have long-term impacts on the surrounding environment.
When lithium batteries burn, they release various toxic gases, mainly including:
- Hydrogen Fluoride (HF):
Hydrogen fluoride is one of the primary toxic gases produced during lithium battery combustion.
It has strong irritant and corrosive properties that can cause severe respiratory damage, ranging from asthma to pulmonary failure.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO):
Carbon monoxide is another common toxic gas that affects blood oxygen-carrying capacity.
- Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN):
Some studies have detected hydrogen cyanide release during lithium battery combustion, which is a highly toxic gas.
- Phosphoryl Fluoride (POF3):
Phosphoryl fluoride is an extremely toxic gas detected in certain lithium battery combustion tests.
- Other Toxic Gases:
Additionally, sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and other toxic gases may be produced. - Flammable Gases:
Besides toxic gases, lithium battery combustion also releases hydrogen, methane, and other flammable gases, increasing fire and explosion risks.
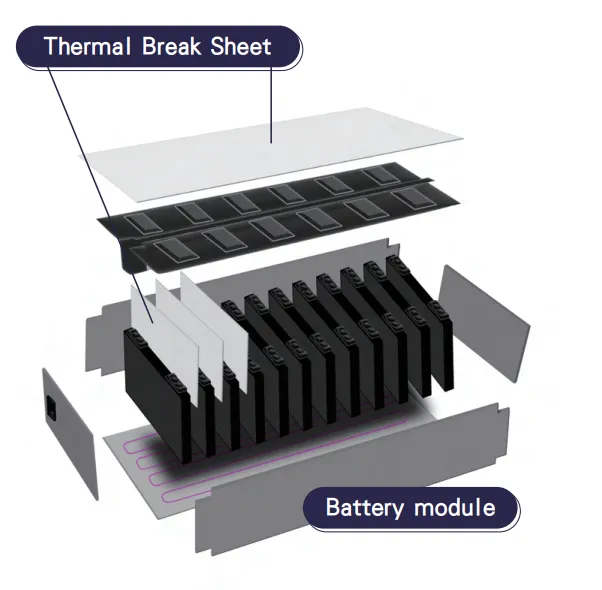
AS27-s: Effective Thermal Insulation Solution for Preventing Thermal Runaway
Facing these potential risks, implementing effective preventive measures is crucial. The AS27-s thermal insulation sheet launched by Sunrise Technology is specifically designed to address this issue.
The AS27-s thermal insulation sheet offers the following advantages:
High-Efficiency Thermal Insulation: Effectively blocks heat transfer, reducing the risk of temperature rise within battery packs.
Flame Retardant Performance: Possesses excellent flame retardant characteristics that effectively suppress fire spread.
High-Temperature Resistance: Maintains stable performance even under extreme temperatures, providing continuous protection for batteries.
Lightweight Design: Does not significantly increase battery pack weight and volume, suitable for various application scenarios.
Customized Solutions: Can be customized according to different battery system requirements to ensure optimal protection.
By using AS27-s thermal insulation sheets in battery packs, the probability of thermal runaway can be significantly reduced. Even under extreme conditions, fire spread can be effectively controlled, substantially reducing potential losses.
Conclusion
As the world increasingly relies on lithium-ion batteries for renewable energy storage and electric transportation, ensuring their safety is paramount. The Moss Landing incident serves as a stark reminder of the potential risks, but also highlights the importance of continued innovation in battery safety technologies.Implementing advanced thermal insulation solutions like AS27-s represents a crucial step towards creating safer, more reliable energy storage systems. As the industry evolves, such measures will be essential in building public trust and supporting the broader transition to sustainable energy solutions.
Related products







